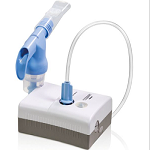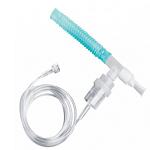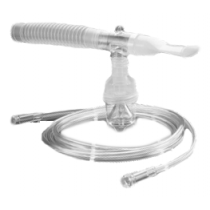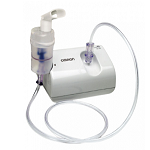
Nebulizers and Compressors
A nebulizer and compressor are components of a medical device used to deliver medication in the form of a mist (aerosol) to the lungs. This is particularly useful for individuals with respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, and other lung diseases. Here’s a detailed explanation of each component and how they work together:
Select Instructions From the List Below
AEROCHAMBER Plus Z STAT Instructions
AeroChamber® VHCs nebulizer. Monaghan is the leader in aerosol delivery with our unique line of AeroChamber® VHCs and Read more...
AireHealth Nebulizer
AireHealth Portable Nebulizer AireHealth’s connected-portable nebulizer is designed to help you be proactive with your therapy, even Read more...
CareFusion AirLife Misty Max 10 Disposable Nebulizer
CareFusion AirLife Misty Max 10 Disposable Nebulize The Airlife efficiently delivers fast and effective treatment to a Read more...
COMPACT COMPRESSOR NEBULIZER Instructions
Pulmo-Aide Compact Compressor The DeVilbiss Pulmo-Aide Compact Compressor is a small footprint unit, which allows for therapy Read more...
Compartment Style Compressor Nebulizer Instructions
Compartment Style Compressor Nebulizer Instructions The Medquip Compartment Style Nebulizer System is easy-to-use and produces fast, effective treatments. With Read more...
Flyp Nebulizer
Flyp Nebulizer Smaller and lighter than a smartphone, Flyp™ nebulizer delivers full-sized effectiveness with pocket-sized portability. It’s Read more...
How to Clean Nebulizer Instructions
Sterilizing Your Nebulizer Parts and Equipment To ensure your safety and increase the effectiveness of treatment, it’s Read more...
How to Use an Aerochamber Instructions
How to use the AeroChamber inhaler This video shows asthma sufferers how to use an aerochamber step Read more...
InnoSpire Essence Nebulizer Compressor Instructions
InnoSpire Essence Nebulizer Compressor Respironics InnoSpire Essence Compressor Nebulizer System features SideStream aerosol technology and provides fast Read more...
InnoSpire Mini Compressor Nebulizer
InnoSpire Mini Compressor Respironics InnoSpire Mini Compressor Nebulizer System is compact and lightweight which enables the patients Read more...
Mabis CompMist Compressor Nebulizer Instructions
Mabis CompMist Compressor Nebulizer The Mabis® CompMist® Compressor Nebulizer offers reliable, quick and efficient delivery of medication Read more...
MABIS CompXP – Nebulizer Instructions
MABIS CompXP – Nebulizer Mabis DMI CompXP Deluxe Portable Handheld Compressor Nebulizer Kit provides powerful respiratory therapy in a Read more...
MABIS® MiniComp™ Compressor Instructions
MABIS® MiniComp™ Compressor Nebulizer Kit MABIS DMI offers a wide range of nebulizers such as the MABIS Read more...
MDI Pocket Chamber Inhaler Spacer Instructions
MDI Inhalers, Spacers MDI are convenient, portable spacers for measured dose inhalers (MDI) used to enhance medication delivery to Read more...
Medneb Compressor Nebulizer
MEDNEB Plus Compressor Nebulizer MedNeb Piston Nebulizers, manufactured by Drive Medical, formerly Medquip, are compressor nebulizer systems for Read more...
Micro Mist Nebulizer Instructions
Micro Mist Hudson Nebulizer Micro Mist Nebulizer is manufactured by Teleflex for respiratory therapy. This nebulizer is easy-to-use, Read more...
Nebulizer Small Volume, Salter Labs Instructions
Salter 8900 Series Disposable Small Volume Jet Nebulizer Salter 8900 nebulizer is a versatile, high performance jet nebulizer used Read more...
Omron CompAir Nebulizer Instructions
Omron NE-C801 CompAIR Compressor Nebulizer CompAIR offers an affordable and efficient alternative for patients experiencing Asthma, COPD Read more...
OptiChamber Diamond Asthma Spacer MDI Inhaler
OptiChamber Diamond Anti-Static Valved Holding Chamber Respironics OptiChamber Diamond Anti-Static Valved Holding Chamber (aVHC) is designed to Read more...
Pacifica Elite Compressor Nebulizer
Pacifica Elite Nebulizer The Pacifica compressor nebulizer is a workhorse with higher liter flows, shorter treatment times and Read more...
Pacifica Elite Nebulizer
PACIFICA ELITE Nebulizer Drive Pacifica Elite Compressor Nebulizer is a workhorse with higher liter flows, shorter treatment Read more...
PARI LC PLUS Nebulizer Set Instructions
PARI LC PLUS nebuliser The efficacy of the PARI LC PLUS nebuliser has been proven in countless studies. It Read more...
PARI TREK S Compact Compressor – Nebulizer
Trek® S Portable Aerosol System The PARI Trek® S Portable Aerosol System is designed from PARI’s long Read more...
Pari Vios Nebulizer Instructions
Pari Vios Nebulizer PARI Vios Nebulizer. Vios Aerosol Delivery System is designed from PARI’s long legacy of clinically Read more...
PARI Vortex Non Electrostatic Asthma Spacer
PARI VORTEX® An affordable valved holding chamber that minimizes the technique and coordination needed for effective inhaler Read more...
Penguin Pediatric Nebulizer Instructions
Penguin Pediatric Nebulizer Drive Medical mq6002r Penguin Pediatric Nebulizer with Carry Bag, and Reusable and Disposable Neb Read more...
Power Neb Ultra Nebulizer Instructions
Power Neb Ultra Nebulizer The Power Neb Ultra Nebulizer by Drive Medical is a perfect addition for patients Read more...
Pulmo-Aide Compact Nebulizer Instructions
Pulmo-Aide® Compact Compressor Nebulizer System The DeVilbiss Pulmo-Aide Compact Compressor is a small footprint unit, which allows for therapy at Read more...
PULMO-AIDE® COMPRESSOR NEBULIZER SYSTEM
Pulmo-Aide® Compact Compressor Nebulizer The DeVilbiss Pulmo-Aide Compact Compressor is a small footprint unit, which allows for Read more...
PULMOMATE® COMPRESSOR NEBULIZER SYSTEM Instructions
PulmoMate® Compressor Nebulizer System The DeVilbiss PulmoMate keeps pace with the world by providing an unbeatable combination Read more...
PulmoNeb LT Compressor Nebulizer Instructions
PulmoNeb LT Compressor Nebulizer When it comes to low cost, high performance compressor nebulizer systems, the remarkable Read more...
Reusable Nebulizer Kit, Drive Medical Instructions
Reusable Nebulizer Kit Anti-spill "T" design Leak-proof and secure seal with simple 1/4 turn assembly design Very low Read more...
Salter AIRE Elite Compressor – Nebulizer Instructions
Salter 8900 Disposable Jet Nebulizer Salter 8900 Series Disposable Small Volume Jet Nebulizer is a versatile, high Read more...
SportNeb 2 Compressor Nebulizer Instructions
SportNeb 2 Compressor Nebulizer The SportNeb 2 Compressor Nebulizer from Drive Medical is a great solution for all Read more...
SPORTNEB™2 NEBULIZER Instructions
SPORTNEB™2 NEBULIZER Drive SportNeb 2 Compressor Nebulizer is designed to efficiently deliver the prescribed saline solution to Read more...
VOCSN Non-invasive Ventilator
VOCSN Ventec Life Systems Ventec Life Systems is defining integrated respiratory care to improve patient outcomes and reduce Read more...
MedExplains AI Content
How to Setup a Nebulizer
A nebulizer is a device that converts liquid medication into a fine mist or aerosol that can be inhaled into the lungs. It consists of several parts:
- Nebulizer Cup:
- This is the chamber where the liquid medication is placed.
- It usually has a lid and a mouthpiece or mask attachment.
- Mouthpiece or Mask:
- The mouthpiece is used to inhale the mist directly into the lungs.
- A mask is used for individuals who may have difficulty using a mouthpiece, such as young children or the elderly.
- Baffle:
- Inside the nebulizer cup, there is often a small component called a baffle that helps to create the mist by breaking up the liquid medication.
Compressor
The compressor is the motorized component of the nebulizer system that generates the airflow required to turn the liquid medication into a mist. It typically includes:
- Air Pump:
- The compressor contains an air pump that generates a continuous stream of compressed air.
- Tubing:
- Flexible tubing connects the compressor to the nebulizer cup.
- The compressed air flows through the tubing into the nebulizer cup.
How They Work Together
- Preparation:
- The liquid medication is placed in the nebulizer cup, and the cup is securely closed.
- The nebulizer cup is connected to the compressor using the flexible tubing.
- The mouthpiece or mask is attached to the nebulizer cup.
- Operation:
- The compressor is turned on, and it begins to pump air through the tubing.
- The airflow enters the nebulizer cup, where it passes through the liquid medication.
- The air pressure causes the medication to form a fine mist, which exits through the mouthpiece or mask.
- Inhalation:
- The patient inhales the mist through the mouthpiece or mask.
- The medication is delivered directly to the lungs, where it can act quickly to open airways, reduce inflammation, or treat infection.
Types of Nebulizers
- Jet Nebulizers:
- These are the most common type and use compressed air to create the aerosol.
- They are generally powered by an electric compressor.
- Ultrasonic Nebulizers:
- These use high-frequency vibrations to create the mist.
- They are usually quieter and more efficient but can be more expensive.
- Mesh Nebulizers:
- These use a vibrating mesh to produce the mist.
- They are compact, portable, and efficient, making them ideal for travel.
Benefits of Using a Nebulizer and Compressor
- Effective Delivery: Provides a direct route for medication to the lungs, making it highly effective for respiratory conditions.
- Ease of Use: Suitable for patients who may have difficulty using inhalers, such as young children or the elderly.
- Versatility: Can be used with a variety of medications, including bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and antibiotics.
Maintenance
- Cleaning: Regular cleaning of the nebulizer cup, mouthpiece/mask, and tubing is essential to prevent infections and ensure proper functioning.
- Replacement: Parts such as the nebulizer cup, tubing, and mask should be replaced periodically as per the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Filter Check: The compressor often has an air filter that should be checked and replaced regularly to ensure clean air supply.
By understanding the components and function of a nebulizer and compressor, patients and caregivers can effectively manage respiratory conditions and ensure optimal medication delivery.
Select Instructions From the List Below
AEROCHAMBER Plus Z STAT Instructions
AeroChamber® VHCs nebulizer. Monaghan is the leader in aerosol delivery with our unique line of AeroChamber® VHCs and Read more...
AireHealth Nebulizer
AireHealth Portable Nebulizer AireHealth’s connected-portable nebulizer is designed to help you be proactive with your therapy, even Read more...
CareFusion AirLife Misty Max 10 Disposable Nebulizer
CareFusion AirLife Misty Max 10 Disposable Nebulize The Airlife efficiently delivers fast and effective treatment to a Read more...
COMPACT COMPRESSOR NEBULIZER Instructions
Pulmo-Aide Compact Compressor The DeVilbiss Pulmo-Aide Compact Compressor is a small footprint unit, which allows for therapy Read more...
Compartment Style Compressor Nebulizer Instructions
Compartment Style Compressor Nebulizer Instructions The Medquip Compartment Style Nebulizer System is easy-to-use and produces fast, effective treatments. With Read more...
Flyp Nebulizer
Flyp Nebulizer Smaller and lighter than a smartphone, Flyp™ nebulizer delivers full-sized effectiveness with pocket-sized portability. It’s Read more...
How to Clean Nebulizer Instructions
Sterilizing Your Nebulizer Parts and Equipment To ensure your safety and increase the effectiveness of treatment, it’s Read more...
How to Use an Aerochamber Instructions
How to use the AeroChamber inhaler This video shows asthma sufferers how to use an aerochamber step Read more...
InnoSpire Essence Nebulizer Compressor Instructions
InnoSpire Essence Nebulizer Compressor Respironics InnoSpire Essence Compressor Nebulizer System features SideStream aerosol technology and provides fast Read more...
InnoSpire Mini Compressor Nebulizer
InnoSpire Mini Compressor Respironics InnoSpire Mini Compressor Nebulizer System is compact and lightweight which enables the patients Read more...
Mabis CompMist Compressor Nebulizer Instructions
Mabis CompMist Compressor Nebulizer The Mabis® CompMist® Compressor Nebulizer offers reliable, quick and efficient delivery of medication Read more...
MABIS CompXP – Nebulizer Instructions
MABIS CompXP – Nebulizer Mabis DMI CompXP Deluxe Portable Handheld Compressor Nebulizer Kit provides powerful respiratory therapy in a Read more...
MABIS® MiniComp™ Compressor Instructions
MABIS® MiniComp™ Compressor Nebulizer Kit MABIS DMI offers a wide range of nebulizers such as the MABIS Read more...
MDI Pocket Chamber Inhaler Spacer Instructions
MDI Inhalers, Spacers MDI are convenient, portable spacers for measured dose inhalers (MDI) used to enhance medication delivery to Read more...
Medneb Compressor Nebulizer
MEDNEB Plus Compressor Nebulizer MedNeb Piston Nebulizers, manufactured by Drive Medical, formerly Medquip, are compressor nebulizer systems for Read more...
Micro Mist Nebulizer Instructions
Micro Mist Hudson Nebulizer Micro Mist Nebulizer is manufactured by Teleflex for respiratory therapy. This nebulizer is easy-to-use, Read more...
Nebulizer Small Volume, Salter Labs Instructions
Salter 8900 Series Disposable Small Volume Jet Nebulizer Salter 8900 nebulizer is a versatile, high performance jet nebulizer used Read more...
Omron CompAir Nebulizer Instructions
Omron NE-C801 CompAIR Compressor Nebulizer CompAIR offers an affordable and efficient alternative for patients experiencing Asthma, COPD Read more...
OptiChamber Diamond Asthma Spacer MDI Inhaler
OptiChamber Diamond Anti-Static Valved Holding Chamber Respironics OptiChamber Diamond Anti-Static Valved Holding Chamber (aVHC) is designed to Read more...
Pacifica Elite Compressor Nebulizer
Pacifica Elite Nebulizer The Pacifica compressor nebulizer is a workhorse with higher liter flows, shorter treatment times and Read more...
Pacifica Elite Nebulizer
PACIFICA ELITE Nebulizer Drive Pacifica Elite Compressor Nebulizer is a workhorse with higher liter flows, shorter treatment Read more...
PARI LC PLUS Nebulizer Set Instructions
PARI LC PLUS nebuliser The efficacy of the PARI LC PLUS nebuliser has been proven in countless studies. It Read more...
PARI TREK S Compact Compressor – Nebulizer
Trek® S Portable Aerosol System The PARI Trek® S Portable Aerosol System is designed from PARI’s long Read more...
Pari Vios Nebulizer Instructions
Pari Vios Nebulizer PARI Vios Nebulizer. Vios Aerosol Delivery System is designed from PARI’s long legacy of clinically Read more...
PARI Vortex Non Electrostatic Asthma Spacer
PARI VORTEX® An affordable valved holding chamber that minimizes the technique and coordination needed for effective inhaler Read more...
Penguin Pediatric Nebulizer Instructions
Penguin Pediatric Nebulizer Drive Medical mq6002r Penguin Pediatric Nebulizer with Carry Bag, and Reusable and Disposable Neb Read more...
Power Neb Ultra Nebulizer Instructions
Power Neb Ultra Nebulizer The Power Neb Ultra Nebulizer by Drive Medical is a perfect addition for patients Read more...
Pulmo-Aide Compact Nebulizer Instructions
Pulmo-Aide® Compact Compressor Nebulizer System The DeVilbiss Pulmo-Aide Compact Compressor is a small footprint unit, which allows for therapy at Read more...
PULMO-AIDE® COMPRESSOR NEBULIZER SYSTEM
Pulmo-Aide® Compact Compressor Nebulizer The DeVilbiss Pulmo-Aide Compact Compressor is a small footprint unit, which allows for Read more...
PULMOMATE® COMPRESSOR NEBULIZER SYSTEM Instructions
PulmoMate® Compressor Nebulizer System The DeVilbiss PulmoMate keeps pace with the world by providing an unbeatable combination Read more...
PulmoNeb LT Compressor Nebulizer Instructions
PulmoNeb LT Compressor Nebulizer When it comes to low cost, high performance compressor nebulizer systems, the remarkable Read more...
Reusable Nebulizer Kit, Drive Medical Instructions
Reusable Nebulizer Kit Anti-spill "T" design Leak-proof and secure seal with simple 1/4 turn assembly design Very low Read more...
Salter AIRE Elite Compressor – Nebulizer Instructions
Salter 8900 Disposable Jet Nebulizer Salter 8900 Series Disposable Small Volume Jet Nebulizer is a versatile, high Read more...
SportNeb 2 Compressor Nebulizer Instructions
SportNeb 2 Compressor Nebulizer The SportNeb 2 Compressor Nebulizer from Drive Medical is a great solution for all Read more...
SPORTNEB™2 NEBULIZER Instructions
SPORTNEB™2 NEBULIZER Drive SportNeb 2 Compressor Nebulizer is designed to efficiently deliver the prescribed saline solution to Read more...
VOCSN Non-invasive Ventilator
VOCSN Ventec Life Systems Ventec Life Systems is defining integrated respiratory care to improve patient outcomes and reduce Read more...